- Dr. Bharatram Dhungana
Background
TAG_OPEN_p_134 Insurance Pokhara University business is considered to be a popular financial tool for risk management. In addition to the personal financial security of human life, it also helps to protect their property and established businesses or institutions from financial risks. Insurance equipment is useful for maintaining economic stability, developing an investment environment and strengthening immunity. Inclusive and robust insurance policies play an important role in promoting insurance literacy and inclusivity.
Despite the expansion TAG_OPEN_p_133 of the insurance business and the increase in monitoring of regulatory bodies, significant progress has not yet been made in the level of insurance access and public awareness in Nepal. In developing countries like Nepal, it is necessary to give priority to ensuring access to insurance for rural and marginalized people as well as workers or laborers associated with the informal sector. A strong insurance system will help develop the insurance market and motivate the general public to engage in insurance literacy and inclusion building activities.
Insurance inclusion has become an important research topic in today’s time and is gradually attracting attention from policy-makers, development partners, and academic circles. Insurance literacy refers to the ability of individuals to understand insurance services, make appropriate decisions, and use insurance services effectively. Many people see insurance as an unnecessary expense unless it is claimed. The importance of insurance in risk management is difficult to understand due to low insurance literacy among the general public. In addition, if the insurance program can be extended to the poor and marginalized sections, they can feel safe. Access and use of effective and inclusive insurance services can help start small businesses, raise income levels and change the socio-economic status of the underprivileged. Maximum efforts for the promotion and inclusion of insurance literacy contribute to the sustainable development of the insurance industry.
Generally, insurance awareness among people living in urban areas is on the rise and they seem to be actively involved in insurance services. However, due to geographical, economic and informational barriers of people living in rural and remote areas, it is difficult to increase access to insurance services. Various studies and researches have shown that many barriers are responsible for the low state of insurance inclusion in Nepal. Limited access to insurance services in rural areas, lack of insurance awareness, lack of accessible insurance services for marginalized people, distrust of insurance providers due to delay in payment of claims and lack of adequate expansion of the insurance market are some of the major hurdles.
Traditional insurance products are not able to address the needs of low-income individuals, workers in the informal sector, marginalized communities, and small farmers. Due to such weaknesses, there is a need to bring an inclusive and accessible insurance plan to make it easier to understand and use insurance services. The role of insurance sector regulatory body (Nepal Insurance Authority) is very important to promote insurance industry in Nepal in a sustainable manner. With increasing risks from climate change, public health crises and economic instability, developing strategies to improve access to insurance and literacy levels has become an urgent need. For this, it is necessary not only to expand the reach and scope of insurance services, but also to provide the necessary knowledge and tools to the citizens to actively engage in insurance services.
TAG_OPEN_p_129 Therefore, the promotion of insurance literacy and insurance inclusion in Nepal needs to be carried forward through the joint efforts of local governments, regulatory bodies, insurance companies, educational institutions and civil society organizations. Such strategies will help develop the foundations for creating an environment of security and investment that insurance provides to every Nepali citizen, irrespective of geographical location or income, by focusing on raising awareness, expanding access, innovation in production, digitization and trust building.
Status of insurance business in Nepal
Looking at the history of insurance business in Nepal, it can be seen that it started with the establishment of Nepal Goods Challan and Insurance Company Limited on Ashwin 8, 2004. According to the importance and need of insurance, the Government of Nepal owned The National Insurance Corporation Pvt. Ltd. in 2024 BS. established. The company was converted into a National Insurance Corporation under the National Insurance Corporation Act, 2025 BS. The company, which was limited to the non-life insurance business, also started operating the life insurance business from 2059 BS.
Similarly, for the first time in Nepal, a joint investment insurance company with foreign investment was established in 2044 BS with the active participation of the private sector. Nepal Life and General Insurance Company Limited has started life and non-life insurance business in Nepal. The company currently provides both types of services as per the provision of having separate companies to carry out life and non-life insurance business. According to the liberal economic policy adopted by the government after the political change of 2046 BS, many private sector-owned insurance companies have been established in Nepal and the recent situation of the insurance companies is depicted in Table 1.
Table 1
Status of insurance companies in Nepal

Source: Nepal Insurance Authority Monthly Statistics, Mid-February, 2081.
As presented in Table 1, there are a total of 37 insurance companies operating in Nepal including 14 life, 14 non-life, 2 reinsurance, 7 micro insurance companies (3 small life insurance, 4 micro non-life insurance) companies. TAG_OPEN_p_124 On the basis of investment, three government investment companies, 29 private sector investment, three branch offices of foreign companies and two joint investment insurance companies are in operation.
B.S. as the regulatory body of the insurance sector in Nepal to make the insurance business systematic, regular, competitive and reliable. The insurance committee was established in 2025 BS. Similarly, efforts were made to promote the Insurance Committee as a strong and autonomous regulatory body by issuing the Insurance Act, 2049 BS. After the amendment of the Insurance Act, 2049 and the Insurance Act, 2079, the Insurance Committee has been transformed into the Nepal Insurance Authority.
Status of access to insurance services in Nepal
The status of access to insurance services in Nepal is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1
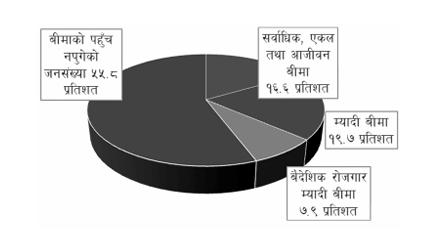
Status of access to insurance services in Nepal
Source: Nepal Insurance Authority Monthly Statistics, Mid-February, 2081.
TAG_OPEN_p_117 Programs and efforts for insurance literacy and inclusiveness The Insurance literacy program provides people with the necessary knowledge and information about the importance and need of insurance. Insurance literacy plays an important role in reaching insurance access to low-income and backward people. It develops the ability to choose a suitable insurance plan by analyzing the benefits and risks of insuring geographically, socially and economically disadvantaged people.
Insurance literacy provides people with the necessary knowledge and skills about what benefits from insurance can be made favorable to their interests and life useful. Insurance literacy includes insurance knowledge, insurance skills, insurance attitude, and insurance behavior. Various studies and researches have concluded that insurance literacy and insurance inclusion have played a role in reducing poverty by expanding services in the country from low-income groups to those without access to financial services. The Insurance Authority of Nepal (INSURANCEA) has already released the Insurance Literacy Framework, 2081 to make the insurance literacy and insurance inclusion program effective. Since the Insurance Literacy Program also contributes significantly to increasing insurance inclusion, it is necessary to extend it to the rural and underprivileged.
The following measures can be followed to effectively reach insurance programs and increase literacy in remote and rural areas of the country:
Local participation: Insurance programs should be mobilized in collaboration with local community leaders, youth groups, and women’s groups. This will attract the local people to the insurance program.
Cheap and favorable plans: Affordable and favorable insurance plans should be offered according to the economic condition of rural and marginalized people.
Digital access: is required to provide insurance services through mobile banking and digital platforms. This will help increase service access in remote areas.
Education and public awareness: Providing insurance information and education materials in the local language will help the local public to understand the importance and usefulness of insurance. In addition, it is necessary to raise awareness about insurance in general by providing information about the benefits of insurance through television, radio, social media and other media.
Government support: Policies and incentive environments to promote insurance programs from the state will help in the development and expansion of the insurance sector. Private and public sector insurance companies need support from the government to reach insurance services to the rural and poor. Similarly, incentive policies should be initiated by the government to increase private and public investment in the insurance sector.
Educational programs: In addition to conducting insurance related education programs in schools, colleges and other educational institutions, it is necessary to establish insurance academies to produce skilled manpower.
Training Workshop: Insurance business can be expanded by organizing workshops to increase insurance literacy through insurance companies, government organizations, and NGOs.
Improving access to insurance: There is a need to increase access to insurance services in rural and remote areas. Digital platforms and mobile applications can be used for this. It is necessary to bring cheap and flexible insurance plans by adapting insurance products to the needs of the people.
Policies and priorities of insurance literacy and inclusiveness
The development and expansion of insurance services guarantees financial security of the risks that may arise on human life, business, property, and liability. Although insurance services have been practiced in Nepal for the last seven decades, a separate insurance policy could not be formulated at the national level. In the past, there was a situation of difficulty in resolving the problems and challenges of the insurance business due to the lack of necessary policies to regulate and guide the insurance sector. The need for an integrated insurance policy was felt for the legal and institutional development of the insurance sector and to minimize the wrong practices in the sector. The government has implemented the National Insurance Policy-2080 to develop the capacity of human resources involved in the insurance business, to make the insurance service fast, fast, quality and effective using modern information technology, and to develop, expand and diversify and promote the insurance sector as per international practice and standards.
The National Insurance Policy seeks to focus on the development of an easy, accessible, reliable, robust and quality insurance system. The goal of the insurance policy is to maintain institutional good governance in the insurance sector by developing and expanding the competitive and reliable insurance system. The seven policies are to develop the insurance sector as a pillar of the economy, to make insurance services easy, simple, accessible, reliable and inclusive, to make the insurance sector modern and competitive, to institutionalize development, expansion and institutional strengthening of the insurance sector, to promote institutional good governance in the insurance sector, to develop the insurance sector as a tool for maintaining financial stability, and to link the insurance sector with the policy of sustainable development and poverty reduction. They are in 2080.
TAG_OPEN_p_104 To develop insurance as a key pillar of the economy, provide financial security for potential risks to human life, health, agriculture, livestock, property and liabilities, reduce the expenditure burden of the state by insuring historical heritage, government property and public liabilities, invest the investable amount of the insurance business in national infrastructure, expand insurance services to the productive sector, for the development and expansion of the insurance business. The policy focuses on collaboration with the local and private sectors.
Similarly, in order to make insurance services simple, easy, accessible and inclusive, expand access to insurance services, include insurance issues in the curriculum at all levels, organize and strengthen the role of insurance service providers and intermediaries so that insurance reaches all service providers, create an environment for the use of modern and high-capacity technology to make insurance arrangements and claim payment process easier and easier; TAG_OPEN_p_103 The focus is on developing an alternative distribution system in insurance, issuing insurance policies through electronic means and expanding the system of claim payment, conducting insurance literacy programs in coordination with the state, local levels and other stakeholders and promoting insurance, providing insurance services through special programs for gender, ethnic, geographical and economically marginalized communities.
To protect the rights of the insured by enhancing the competitive capacity of the insurer to develop insurance in accordance with international standards by making it modern and competitive, adopting an international standard accounting system in the insurance sector, effectively adopting the basic principles of universally accepted insurance, developing a modern insurance system according to international good practice and exchanging cooperation with international organizations related to insurance. There seems to be an emphasis on doing it.
Strengthening and enabling the insurance regulatory bodies for institutional strengthening, development and expansion of the insurance sector, formulating and implementing periodic plans, standards and programs for improving the insurance sector, promoting the health insurance business to strengthen social security, enhancing the institutional capacity of the insurer, emphasizing research and development for the development, expansion and diversification of the insurance sector; The policy has also given priority to the establishment of insurance desks and insurance units at the state government and local levels, establishment and promotion of insurance institutions, institutes and colleges to develop skilled manpower in the insurance sector.
Formulate and implement the code of conduct of insurance regulatory bodies, insurers, insurance intermediaries and other insurance service providers to promote institutional good governance in the insurance sector, enhance the regulatory capacity of the insurance sector, strengthen the internal control system of the insurer, make arrangements for the insurer to bear social responsibility, maintain accountability and transparency in the insurance sector, implement risk-based supervision system in the insurance sector; The national insurance policy focuses on making the regulation and monitoring system based on the latest information system, discouraging money laundering and terrorist financing through the insurance business, making insurance intermediaries accountable and accountable to the insured.
Under the policy of developing insurance as a powerful tool to maintain financial stability, make and implement a key performance indicator to measure the financial health of the insurer, implement risk-based capital system in the insurance business, enable foreign exchange earnings by strengthening and competitive the domestic reinsurance business, expanding the scope of reinsurance to increase the risk bearing capacity of the insurance sector, The use of financial instruments such as disaster bonds, insurance bonds, green bonds to reduce risk and increase the country’s financial resources, to establish a collective insurance fund (insurance bridge) such as earthquake, air, agriculture, microinsurance to increase the total holding capacity of the insurance sector has been given priority.
TAG_OPEN_p_98 Finally, expand insurance services to link the insurance sector with sustainable development and poverty reduction, help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals and reduce poverty through insurance services, create more jobs by reducing the commercial risk of micro and small industries, link the risks from climate change with insurance services, provide special types of insurance services to reduce the risk arising from natural disasters; There is a need to focus on diversification and localization of insurance policies based on geographical and social environment, providing special facilities including subsidy on insurance to the people living below the poverty line, expanding insurance services in the environmentally and economically vulnerable businessmen, small farmers, producer groups and cooperative sectors, and making arrangements to insure Nepalis living abroad.
The role of The Insurance Authority of Nepal is important for the effective implementation of TAG_OPEN_p_97 the insurance policy. It is necessary to make contemporary reforms, modifications and revisions in the policy based on the results obtained, the experience of implementation and the relevance, suitability and overall effectiveness of the policy within five years of the commencement of the implementation of the policy. In the country’s periodic plan and annual budget, it is necessary to ensure access to insurance services to the common people by developing the sustainable insurance sector as well as creating an environment to implement this policy provision.
Conclusions and suggestions
For the sustainable development TAG_OPEN_p_95 of the insurance sector in Nepal, it is necessary to expand insurance literacy and insurance inclusion and reach out to the rural and underprivileged. With more than half of nepal’s population still out of reach of insurance, the state needs to focus on expanding insurance services to economically, socially and geographically disadvantaged sections or communities. Due to lack of necessary information about insurance, distrust and lack of financial literacy, some people are not able to come under the purview of insurance. In order to effectively implement the ‘Insurance Literacy Framework-2081’ issued by the Nepal Insurance Authority, it is necessary to take the insurance literacy program to the villages and homes as a national campaign by using digital technology, adopting international standards and conducting programs according to local needs. It is necessary to conduct insurance literacy programs in the target communities with the joint efforts of the Government of Nepal, regulatory bodies, insurance companies and the private sector. In addition, subsidies on insurance services, subsidized premiums and the development of a simple claim payment system will help expand access to insurance. In order to make the insurance sector sustainable, efforts should be made to make citizens of all levels aware of the importance of insurance and bring them under the purview of insurance. Since it is difficult to achieve success in the sustainable development of the insurance sector only through the sole efforts of the state, it is necessary to move forward by mobilizing active cooperation and participation of all sectors. At the same time, it is imperative to develop the insurance sector as a major pillar of the country’s economy by advancing the campaign to increase insurance literacy and inclusion.
Brief introduction to the author
Dr. Bharat Ram Dhungana is an associate professor at Pokhara University. He completed his PhD in Finance in 2015, has more than 20 years of experience in the field of teaching and research, has published research articles in three dozen renowned national and international journals, published various articles in national-level dailies like Kantipur, Gorkhapatra, Business Daily, etc., and presented more than a dozen research papers at national and international level conferences. is.
(Note: This article has been adapted from insurance news and views published on the occasion of the 57th anniversary of Nepal Insurance Authority.) )























